- Home
- Technologies
- Ultisep
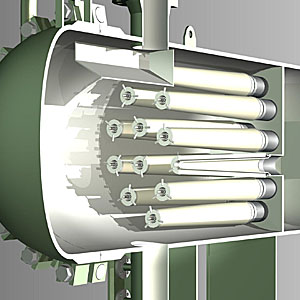
UltiSep flows from the inside-to-the-outside, reducing the gas velocity as the droplets are being removed. Capital costs are directly related to the size of the housings required for a particular gas flow rate. An evaluation of the factors affecting vessel sizing indicated that the annular space surrounding the exterior of the element is a key variable in the design.
The annular space controls the annular velocity of the treated gas. If this annular velocity exceeds certain critical thresholds, the gas will re-entrain or shatter droplets that are not adequately being drained from the system. In a system using conventional cylindrical elements, the annular velocity of the exiting gas increases along the element with a maximum velocity at the closed end of the element.
Benefits
- Effectively removes liquid aerosols from gas streams
- Provides effective separation from nano-levels to that approximating a demister pad
- Reduces gas velocity as droplets are removed
- Addresses inherent deficiencies of conventional gas-liquid separators
-
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
-
The Apex element is specifically intended to keep annular velocities constant across the entire height of the element. This was accomplished by introducing a gentle taper in the element, so that the annular space on the outside of the element gradually increased from the bottom to top, keeping pace with the external gas flow as it exited the element.
-
FIELDS OF APPLICATION
-
- Phase separation and condensation
- Compressor lube-oils from compression
- Chemical addition to pipelines (including corrosion inhibitors)
- Entrainment from overheads of contact towers resulting in aerosol distributions primarily in the nanometer range
- UltiSep was designed to effectively separate these contaminants and is in service protecting high-value installations and systems worldwide.
RELATED APPLICATIONS
The key aspects of an alkylation unit pertain to the amount of acid that needs to be made-up on a continuing basis. This cost becomes even more critical if the plant has no onsite acid regeneration, or the acid consumption exceeds the acid regeneration capacity.
Fuel Gas Streams are frequently contaminated with liquid aerosols. The liquid exists as a stable and persistent “smoke” in the gas stream.
The key to optimizing a hydroprocessing unit is to maximize the life of the catalyst bed and increase energy efficiency of the furnaces.
Until recently, the Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) market was a relatively small part of the gas processing world. The market has experienced a transformation fueled by the discovery of vast reserves in North America, Asia’s robust economic growth, larger populations, and the demand for cleaner energy.
There are a number of factors that affect the capacity and operation of a typical amine system. Solid or liquid contaminants in the system may cause foaming. The presence of foaming is typically addressed by the addition of expensive antifoam chemicals and/or by reducing the operating capacity of the amine system.
Glycol dehydration is a liquid desiccant system for the removal of water from natural gas and natural gas liquids (NGL).
Natural gas gathering systems deliver large volumes of gas via pipeline to the central inlet of the gas processing facility. Removal of solid contaminants and free liquids present in the inlet gas is critical to the downstream process.









