- Home
- Technologies
- Apex Zenith
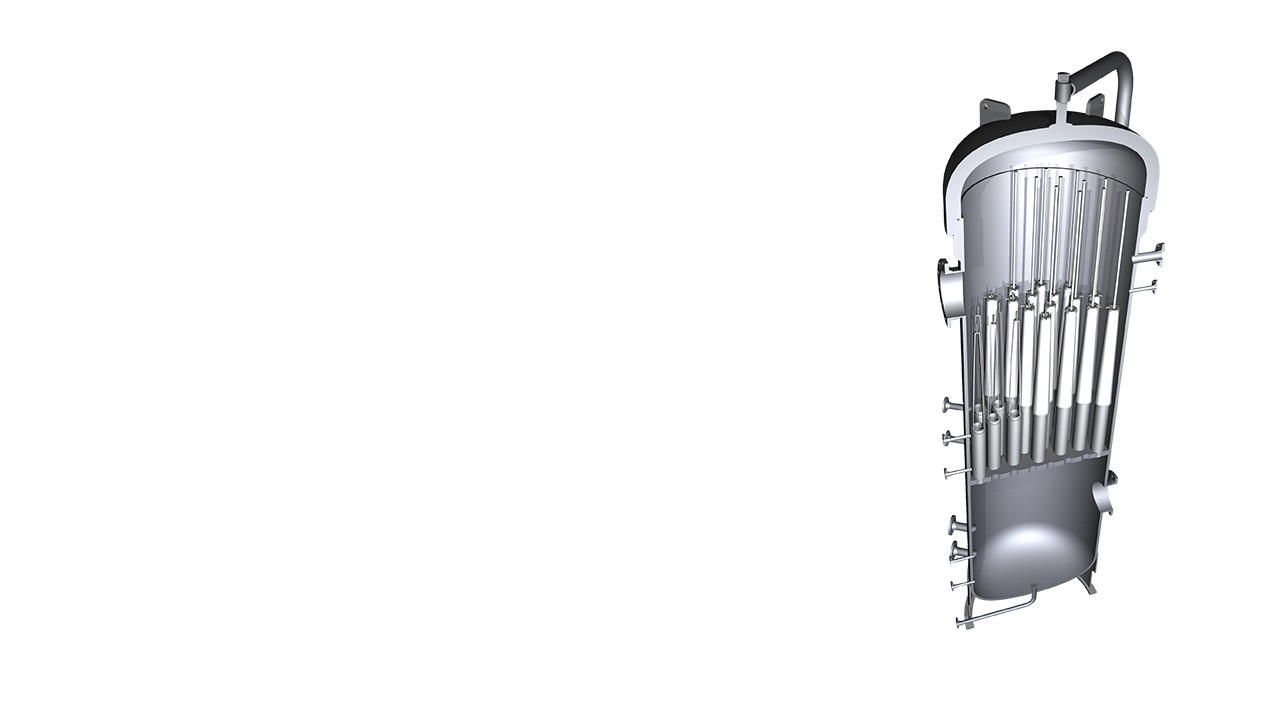
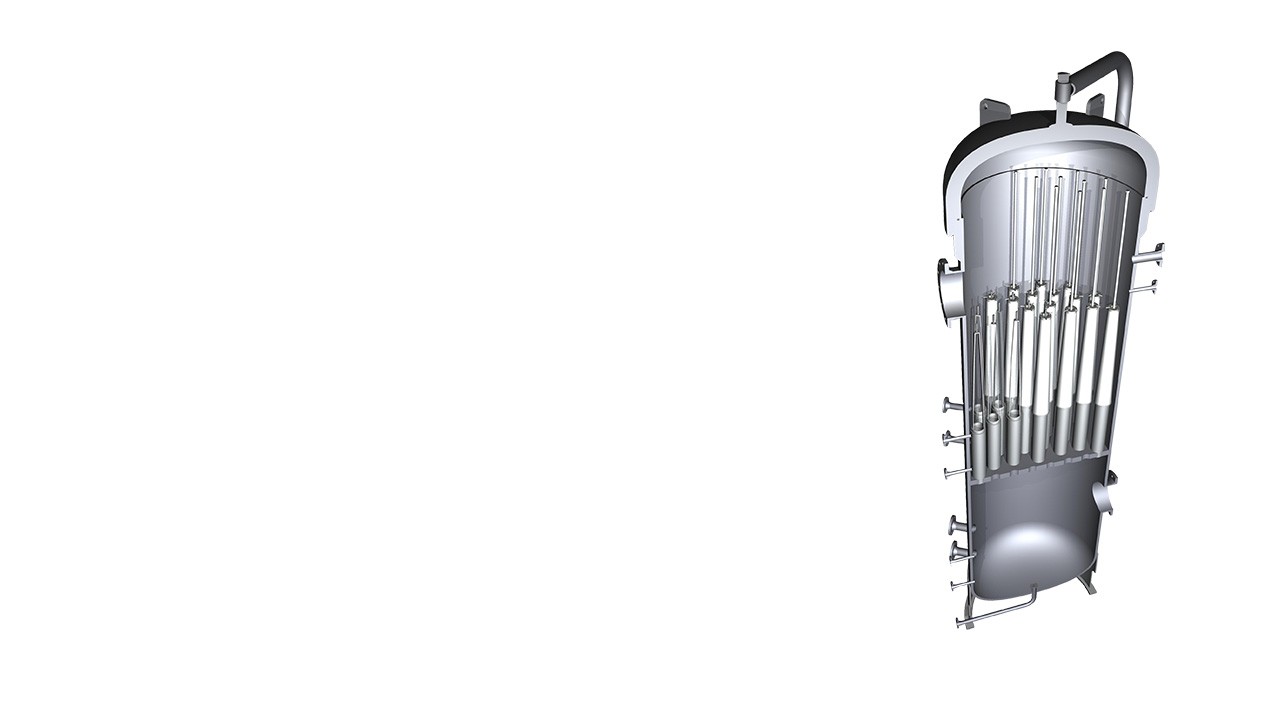
Pentair UltiSep technology featuring Pentair Apex separation media enables gas-processing facilities to achieve superior separation efficiency of aerosol contamination, leading to increased throughput and operational efficiencies. Building upon this legacy of separation expertise and industry-leading performance, Pentair has developed the next generation of liquid gas separation technology for midstream and downstream plants, Pentair Apex Zenith element filters.
Separation system efficiency is determined by the combination of gas velocity/flow rate, the amount of aerosol ingression in the gas, the operating pressure and internal element configuration. As the flow rate and/or liquid loading increase, efficient separation of liquids becomes more difficult. Pentair Apex Zenith coalescing element is enabled by our proprietary advanced media that delivers higher separation efficiencies at significantly elevated gas velocities and liquid concentrations with a reduced vessel envelope.

Features
- New proprietary media that can deliver extremely high separation efficiencies at significantly elevated gas velocities and liquid concentrations with a reduced vessel envelope
- Reduced surface energy material that lowers interfacial tension even in the presence of elevated gas velocities
- Droplet interception as small as 0.1 micron
- Separation Efficiency > 99.99%
- Accommodate 50% greater gas velocity and liquid loading within a smaller vessel envelope
- Reduced capital expenditure with significantly minimized footprint compared to conventional systems
- Specially designed materials accelerate the draining process for captured liquids
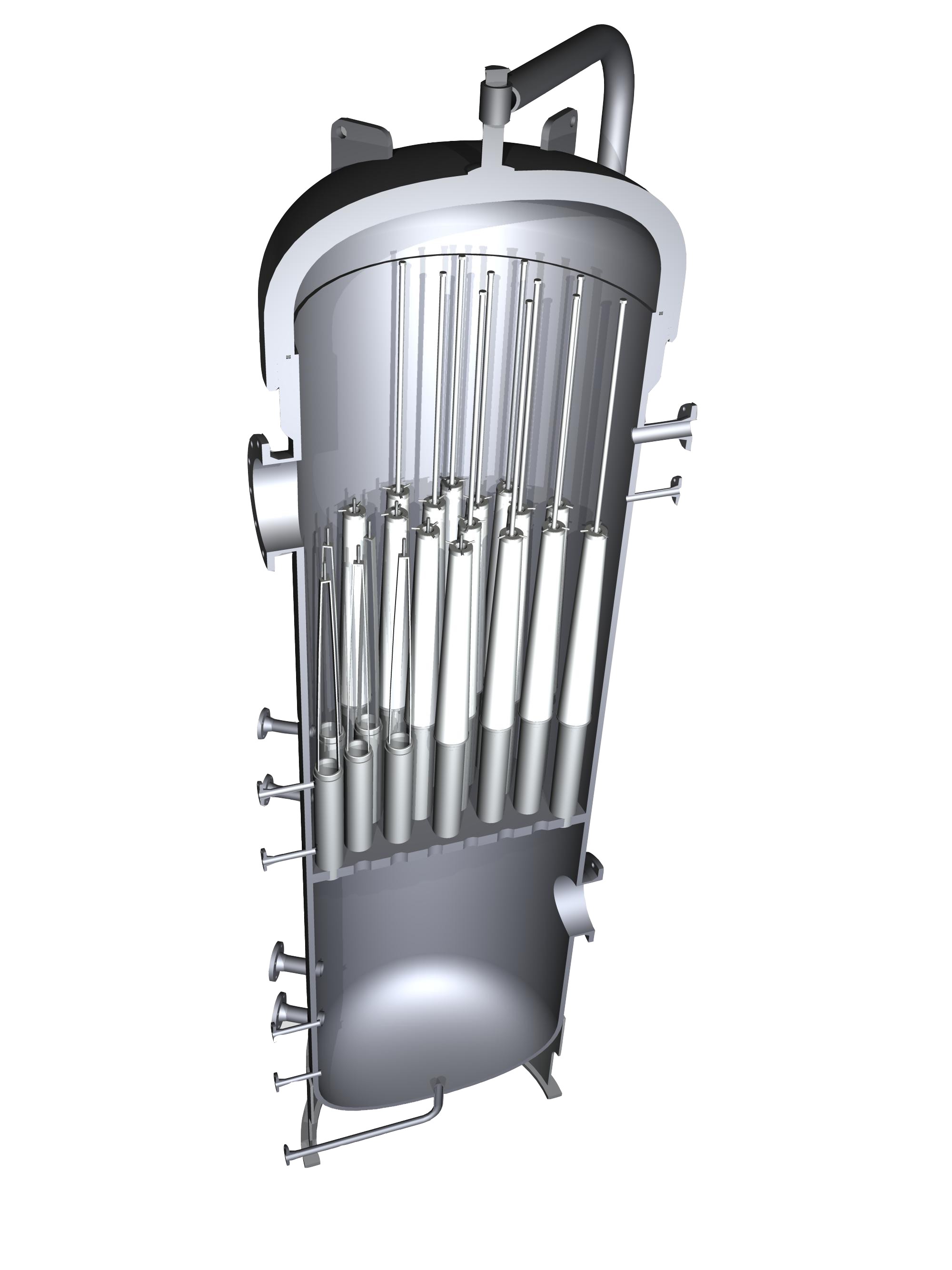
How An UltiSep Works
- Wet gas containing both bulk liquids and liquid aerosol enters the UltiSep system through the lower nozzle into the bottom chamber of the vessel.This chamber is designed to allow bulk liquids to slow as the velocity of the gas slows and drop to the bottom of the chamber. Level controls and drain ports are located at the bottom of the lower chamber to remove bulk liquids.
- Once bulk liquid falls out in the lower chamber, the “wet gas” or gas entrained with liquid aerosols moves up through the tubesheet into the elements themselves. The elements flow from in to out, and as the wet gas begins to exit the element, the specialized coalescing media captures these sub-micron aerosols and holds them, combining them with other droplets until they are large enough to be drained.
- Liquid captured in the elements drains downward, dripping between elements to the bottom of the upper chamber. There, liquid is collected and another set of level controls and drain ports removes this coalesced liquid.
- The elements are mounted on risers, keeping them out of this coalesced liquid so that they will never be submerged when the level controls are operating correctly.
- Dry gas, removed of 99.97+ percent of all liquids, exits the elements and moves upward, exiting near the top of the vessel.
| Title | Download PDF | |
| Brochure | BROC PENTAIR APEX ZENITH 2020 LR |
Download |
Reduce vessel size and footprint with Apex Zenith
Achieve better separation performance with Pentair’s Apex Zenith Coalescing Elements—the next generation of our apex technology.
RELATED APPLICATIONS
The key aspects of an alkylation unit pertain to the amount of acid that needs to be made-up on a continuing basis. This cost becomes even more critical if the plant has no onsite acid regeneration, or the acid consumption exceeds the acid regeneration capacity.
BTX (BENZENE, TOLUENE AND XYLENE)
Purify benzene, toluene, and xylene (BTX) from refinery or petrochemical aromatics streams such as catalytic reformate or pyrolysis gasoline. This liquid-liquid extraction processes offers lower capital and operating costs, simplicity of operation, range of feedstock, and solvent performance.
Reactor products can contain gelatinous, deformable solids form in coating formulation. Batch Process: Limited reactor turn-over (constrained through-put) due to long filtration process. Reduce operating costs and batch cycle time, double capacity and increase online life.
Silicones are inert, synthetic compounds with a variety of forms and uses. Typically heat-resistant and rubber-like, they are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medical applications, cookware, and insulation.
Proper fluid and proppant placement are critical to a successful propped fracture stimulation treatment.
The key to optimizing a hydroprocessing unit is to maximize the life of the catalyst bed and increase energy efficiency of the furnaces.
Many lube oil recovery processes create aqueous and hydrocarbon emulsions that are difficult to separate by means of conventional liquid/liquid separations technology.
Hydrocarbons in the sour water system are typically present on a continuous basis at up to 10,000 ppm and during upsets to levels greater than 50,000 ppm.
There are a number of factors that affect the capacity and operation of a typical amine system. Solid or liquid contaminants in the system may cause foaming. The presence of foaming is typically addressed by the addition of expensive antifoam chemicals and/or by reducing the operating capacity of the amine system.
The key aspects of a caustic treating system pertain to the degree of contact between the caustic and hydrocarbon to facilitate the mass transfer.
Eliminate hydrocarbons in Quench Water system, minimize fouling, provide greater system reliability, lower maintenance, lower energy costs.
Product custody transfer involves a number of processes, all of which are intended to meet transfer specifications in terms of water, particulate and metals.
Fuel Gas Streams are frequently contaminated with liquid aerosols. The liquid exists as a stable and persistent “smoke” in the gas stream.
Glycol dehydration is a liquid desiccant system for the removal of water from natural gas and natural gas liquids (NGL).
Natural gas gathering systems deliver large volumes of gas via pipeline to the central inlet of the gas processing facility. Removal of solid contaminants and free liquids present in the inlet gas is critical to the downstream process.
There are two basic steps to the treatment of natural gas liquids in the natural gas stream. First, the liquids must be extracted from the natural gas. Second, these NGLs must be separated themselves.