- Home
- Technologies
- Liquisep
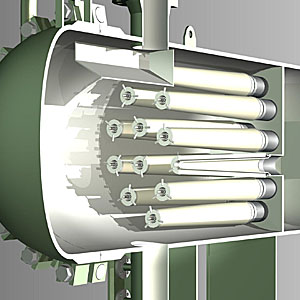
LiquiSep technology has been implemented specifically to help separate emulsions that are not separable by conventional coalescers.
Conventional coalescers are unable to provide the degree of clarity associated with LiquiSep technology due to the inability to capture and remove the most penetrating droplets that cause carry-over. LiquiSep can separate these dispersed and emulsified droplets from the hydrocarbon to practically non-detectable levels.
Advances in the technology now permit horizontal installations, further reducing capital cost. The effluent from a typical LiquiSep separation consists of two separate phases: one phase is a clear product hydrocarbon stream, and the second phase is a clear product aqueous stream.
Benefits
- Advanced emulsion separation
- Cost efficiency high-quality output
- Scalability and modularity
- Operation flexibility
- Environmental and economic benefits
-
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
-
The Apex element is specifically intended to keep annular velocities constant across the entire height of the element. This is accomplished by introducing a gentle taper in the element, so that the annular space on the outside of the element gradually increases from the bottom to top, keeping pace with the external fluid flow as it exits the element.
The high fluid velocities at the circumference of the cylindrical element require the cylindrical elements to be spaced further apart. Apex elements do not have to be spaced as far apart, allowing the same flows to be handled in a smaller vessel, implying lower capital costs.
Addressing Aqueous Contamination
Hydrocarbon systems frequently encounter aqueous contamination. The aqueous component typically exceeds the soluble limit and accumulates within the hydrocarbon as a separate dispersed and emulsified phase. This stable emulsion is typically observed as a stable haze.
Challenges with Conventional Separation Mechanisms
The challenge associated with conventional separation mechanisms is that they depend on capturing the droplets through impaction of the droplet on a separation medium (such as wire mesh or filter media). As the droplets become smaller, the boundary layers around such media increase in dimension to the point that the droplets are much more likely to move around the fiber rather than collide into it. The capture of such fine droplets, then, requires advances in technology to reduce such boundary layers, as well as create additional mechanisms for droplet capture.
RELATED APPLICATIONS
The key aspects of an alkylation unit pertain to the amount of acid that needs to be made-up on a continuing basis. This cost becomes even more critical if the plant has no onsite acid regeneration, or the acid consumption exceeds the acid regeneration capacity.
The key aspects of a caustic treating system pertain to the degree of contact between the caustic and hydrocarbon to facilitate the mass transfer.
Eliminate hydrocarbons in Quench Water system, minimize fouling, provide greater system reliability, lower maintenance, lower energy costs.
Product custody transfer involves a number of processes, all of which are intended to meet transfer specifications in terms of water, particulate and metals.
Many lube oil recovery processes create aqueous and hydrocarbon emulsions that are difficult to separate by means of conventional liquid/liquid separations technology.
Until recently, the Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) market was a relatively small part of the gas processing world. The market has experienced a transformation fueled by the discovery of vast reserves in North America, Asia’s robust economic growth, larger populations, and the demand for cleaner energy.
BTX (BENZENE, TOLUENE AND XYLENE)
Purify benzene, toluene, and xylene (BTX) from refinery or petrochemical aromatics streams such as catalytic reformate or pyrolysis gasoline. This liquid-liquid extraction processes offers lower capital and operating costs, simplicity of operation, range of feedstock, and solvent performance.
Reactor products can contain gelatinous, deformable solids form in coating formulation. Batch Process: Limited reactor turn-over (constrained through-put) due to long filtration process. Reduce operating costs and batch cycle time, double capacity and increase online life.
Silicones are inert, synthetic compounds with a variety of forms and uses. Typically heat-resistant and rubber-like, they are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medical applications, cookware, and insulation.
The key to optimizing a hydroprocessing unit is to maximize the life of the catalyst bed and increase energy efficiency of the furnaces.
There are two basic steps to the treatment of natural gas liquids in the natural gas stream. First, the liquids must be extracted from the natural gas. Second, these NGLs must be separated themselves.













